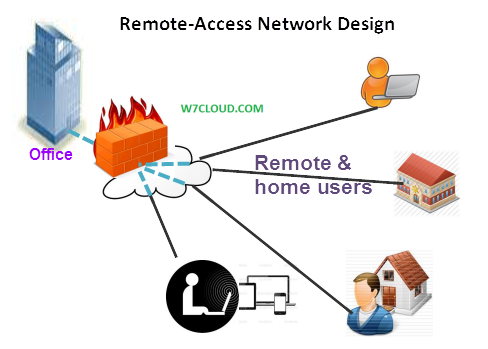
One of the goals of remote-access network design is to provide a unified solution that allows for seamless connectivity to remote users. This article is about the providing remote access to users which are not in office, with this remote access these users may able to access their office’s network from home or from other offside location. The primary function of remote access is to provide access to your users to internal resources and applications. Because connection requirements drive the technology selection process, it is important that you analyze the application and network requirements in addition to reviewing the available service provider options.
The following summarizes typical remote-access requirements:
- Best-effort interactive and low-volume traffic patterns
- Connections to the enterprise edge using Layer 2 WAN technologies
- Voice and IPsec VPN support
Remote-access network connections are enabled over permanent always-on connections or on-demand connections. Technologies include digital subscriber line (DSL), cable, wireless 802.11 a/b/g/n LAN, and 3G/4G wireless WAN (WWAN). However, these remote-access technologies might or might not be available, so it is best to check the availability for the location in your network design.
VPN is one of the best way to provide the remote access to your remote user. While providing the VPNs access to your customer to your office you can use the following three methods:
Overlay VPNs: this VPN overlay the customer existing point to point network, these VPNs are very common and simple to set up. Overlay VPN are point to point link and have virtual circuit (PVC) and normally these are low cost VPNs solutions.
VPDN’s: VPDN is the type of VPN which relay on security domain of the ISP, it uses the vendor’s dial-in solutions for private dialup connection so you can connect to the local service provide edge by using modem, ISDN etc then service provide pull all the traffic from their point of presence to customer own router. VPNs tunnel can be create with the Cisco L2F, PPTP and L2TP.
Peer to peer VPNs:
These VPNs use the MPLS, for more details you can review RFC 2547.
When you need to provide secure remote access using VPNs, you must consider several things. One key consideration is the use of enterprise VPNs or service provider based VPNs.
Here are some technology options that are available when selecting VPNs.
Enterprise VPNs
Here is a list of VPNs that can be found in enterprise environments:
- IP Security (IPsec)
- Cisco Easy VPN
- Generic routing encapsulation (GRE)
- Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network (DMVPN)
- Virtual tunnel interface (VTI)
- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol Version 3 (L2TPv3)
Service Provider VPNs
Here is a list of VPNs that can be found with most SPs:
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
- Metro Ethernet
- Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS)
IPSec VPN:
IPSec is a group of security protocols for encrypting IP packets between two hosts and thereby creating a secure tunnel. IPSec uses open standards and provides secure communication between peers to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity through network layer encryption. IPSec VPNs are commonly configured between firewalls and routers that have IPSec features enabled.
The IPSec protocols include Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP), Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH). IPSec uses symmetrical encryption algorithms to provide data protection. Internet Key Exchange (IKE) ISAKMP protocols provide secure method to exchange keys. ESP is used to provide confidentiality, data origin authentication, connectionless integrity, and anti-replay services. AH is used to provide integrity and data origin authentication, usually referred to as just authentication. Here you can review an example of IPSEC VPN on GNS3.
Cisco Easy VPN:
Although VPNs provide a high level of authentication and encryption of data between endpoints, it also increases the complexity for the end user to set up and configure. Cisco Easy VPN remote feature reduces the difficultly with setting up VPN endpoints by using the Cisco VPN Client protocol. This allows most of the VPN parameters to be defined at the Cisco Easy VPN Server. After the Cisco Easy VPN Server has been configured, a VPN connection can be set up with a simple configuration on the Cisco Easy VPN remote. The remote feature is available on the Cisco 800 series Routers (ISR).
IPSec DMVPN:
DMVPN is a Cisco IOS solution for building IPsec + GRE VPNs in a dynamic and scalable manner.
DMVPN relies on two key technologies called NHRP and mGRE:
Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) creates a mapping database for all spoke tunnels to real public addresses.
Multipoint GRE (mGRE) is a single GRE interface, which provides support for multiple GRE, and IPSec tunnels to reduce the complexity and the size of the configuration.
DMVPN supports a reduced configuration framework and supports the following features:
- DMVPN support IP unicast, IP multicast, and dynamic routing protocols
- Remote spoke routers with dynamic IP addressing
- Spoke routers behind dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT) and hub routers behind static NAT
- Dynamic spoke-to-spoke tunnels for partial scaling or fully meshed VPNs
- Support for all of the GRE tunnel benefits such as QoS, deterministic routing, and redundancy scenarios
Each remote site is connected using a point-to-point (P2P) GRE tunnel interface to a single mGRE headend interface. The headend mGRE interface dynamically accepts new tunnel connections.
IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface (VTI):
Virtual tunnel interface (VTI) is a new IPsec VPN design option available in Cisco IOS software. VTI has some interesting advantages over previous IPsec design options, including support for dynamic routing protocols and IP multicast without using GRE or mGRE type interfaces. Also, VTI tunnels are assigned an unique interface, specific tunnel level features such as QoS can be configured for each tunnel separate from other VTI tunnels.
Metro Ethernet:
Many ISPs are offering Metro Ethernet services for providing the high bandwidth for MAN (metropolitan area network); these are based on Ethernet, IP, and optical technologies such as dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM). Metro Ethernet services can provide more bandwidth, the ability to upgrade the bandwidth as needed and higher levels of redundancy through multiple route processors.
MPLS:
MPLS provide a fast method for transferring the packet in data network by assigning labels. MPLS can run on many L2 technologies, including ATM, Frame Relay, PPP, Packet over SONET (POS), and Ethernet.
MPLS Layer 3 VPNs have the following characteristics:
The MPLS network distributes labels to each VPN.
- Only labels for other VPN members are distributed.
- Each VPN is automatically provisioned by IP routing.
- Each MPLS network is as secure as Frame Relay connections.
- Encryption can be added to the VPN to provide privacy.
- Only one label for both for QoS and VPN is needed.